Key Takeaways
Blockchain in aviation ensures secure, tamper-proof data sharing, improving trust, audit readiness, and operational transparency across airlines, airports, and regulators.
The role of blockchain in aviation reduces fraud and errors through traceable records for maintenance, supply chain, compliance, and financial settlements.
Smart contracts automate refunds, payments, and agreements, cutting delays, lowering costs, and improving efficiency across aviation operations.
Early blockchain adoption prepares aviation systems for future technologies like AI, IoT, and data-driven decision-making.
Aviation companies should begin with high-impact use cases such as MRO, parts traceability, or identity management, then scale securely.
JPLoft builds secure, scalable blockchain aviation systems that meet compliance needs and support long-term aviation software growth.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple systems in a secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant way. Each transaction is stored in linked blocks, verified through consensus, and protected by cryptographic methods, eliminating the need for a central authority.
In the aviation industry, blockchain adoption is rising as airlines, airports, and regulators seek secure data sharing, traceable records, and automated processes. Its ability to ensure transparency, prevent fraud, and streamline operations is driving growing interest across ticketing, maintenance, and compliance systems.
If you decide to create aviation software, learning about the aviation blockchain market will provide you with a complete overview of the technology.
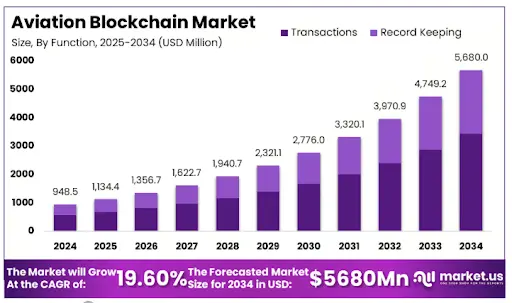
-
The global aviation blockchain market is expected to be worth around USD 5680 million by 2034. This market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 19.6% during the forecasted period from 2025 to 2034.
-
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the aviation blockchain sector, capturing over 36.9% of the global market share, which is equivalent to USD 349.9 million in revenue.
-
Additionally, the US aviation blockchain market is expected to grow at a robust CAGR of 21.3%.
To build an airline reservation system, learning about the market stats is not a limitation. Let's consider the complete list of the importance of blockchain in the aviation industry in the proceeding section.
Benefits of Blockchain in the Aviation Industry
Blockchain brings transparency, security, automation, and trust to aviation operations by enabling tamper-proof data sharing, streamlined processes, and reliable collaboration across airlines, airports, and aviation software systems.
Let’s evaluate the complete benefits of blockchain in the aviation industry below.
1. Improved Data Security and Integrity
One of the biggest benefits of blockchain in the aviation industry is secure, tamper-proof data storage.
Blockchain ensures that flight records, passenger data, and operational logs cannot be altered without authorization. This reduces data breaches, fraud, and unauthorized system access across airlines and airports.
2. Transparent and Traceable Supply Chain
Blockchain creates a single source of truth for aircraft parts and components. Maintenance records, part origins, and service history can be tracked end-to-end.
This improves safety, reduces counterfeit parts, and highlights the importance of blockchain in the aviation industry supply chain management.
3. Streamlined Aircraft Maintenance and MRO
Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul processes benefit from immutable blockchain records. Every inspection, repair, and replacement is permanently logged and easily auditable.
This improves regulatory compliance, minimizes manual paperwork, and reduces maintenance-related delays.
4. Faster and More Secure Passenger Identity Management
Blockchain enables secure digital identity verification for passengers. Boarding, immigration checks, and access control become faster and more reliable.
This use case highlights the benefits of blockchain in the aviation industry's passenger experience and airport efficiency.
5. Automation Through Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate processes such as ticket refunds, insurance claims, leasing agreements, and vendor payments.
These contracts execute automatically when conditions are met. This reduces disputes, speeds up settlements, and lowers operational costs for aviation stakeholders.
6. Enhanced Regulatory Compliance and Audits
Aviation regulators require accurate, verifiable records. Blockchain provides real-time access to certified data for audits and inspections.
This strengthens trust between airlines, airports, and authorities, reinforcing the importance of blockchain in aviation industry compliance frameworks.
7. Reduced Operational Costs and Process Delays
By eliminating intermediaries and manual reconciliations, blockchain cuts administrative overhead. Faster data sharing between airlines, airports, suppliers, and regulators reduces delays.
Over time, this efficiency becomes one of the strongest long-term benefits of blockchain in the aviation industry.
Role of Blockchain in Aviation
Blockchain in aviation helps in aircraft maintenance, secures data management, helps in regulatory compliance, improves cybersecurity, and helps in revenue management.
Let’s evaluate the complete list of roles of blockchain in aviation, below.
1] Secure Data Management Across Aviation Systems
Aviation generates massive volumes of sensitive data, from flight operations to passenger records. Thus, one of the crucial roles of Blockchain in the aviation industry is to ensure this data is stored in tamper-proof, immutable ledgers.
In aviation software, this creates a trusted data layer where airlines, airports, and regulators can access accurate information without duplication or manipulation.
2] Aircraft Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Management
The role of Blockchain in aviation software is to enable permanent, traceable maintenance records for aircraft and components. Every inspection, repair, and replacement is logged securely and shared across stakeholders.
Aviation software integrated with blockchain improves maintenance planning, compliance audits, and reduces risks linked to incomplete or altered records.
3] Aviation Supply Chain and Parts Traceability
The aviation supply chain depends on the authenticity and traceability of parts. Blockchain tracks components from manufacturer to installation, preventing counterfeit parts.
Aviation software using blockchain provides real-time visibility into part history, certifications, and lifecycle status, improving safety and operational confidence.
4] Passenger Identity and Travel Verification
Blockchain supports secure digital identities for passengers, reducing dependency on manual checks. Identity data can be verified instantly without exposing personal information.
Aviation software built on blockchain improves airport security, speeds up check-in and boarding, and supports seamless travel experiences.
5] Smart Contracts for Automated Aviation Processes
Smart contracts automate processes like ticket refunds, insurance claims, aircraft leasing, and vendor payments. These contracts execute automatically when predefined conditions are met.
In aviation software, this reduces disputes, eliminates delays, and lowers administrative overhead across airline operations.
6] Regulatory Compliance and Audit Transparency
Aviation authorities require strict compliance and detailed reporting. Blockchain provides regulators with real-time, verifiable access to operational data.
Aviation software using blockchain simplifies audits, ensures compliance accuracy, and reduces manual documentation efforts for airlines and airports.
7] Cybersecurity and Fraud Prevention
Aviation systems are frequent targets for cyber threats and fraud. Blockchain decentralizes data control, reducing single points of failure. Another role of blockchain technology in aviation software is fraud prevention and cybersecurity.
When cybersecurity is integrated into aviation software, it strengthens cybersecurity, prevents unauthorized changes, and improves resilience across critical digital infrastructure.
8] Integration Layer for Advanced Aviation Technologies
Blockchain acts as a trusted backbone for integrating AI, IoT, and predictive analytics in aviation. Sensor data, AI insights, and operational decisions can be recorded transparently.
This role makes blockchain essential for future-ready aviation software designed for automation, intelligence, and scale.
9] Revenue Management and Financial Settlement
Blockchain improves transparency in revenue sharing between airlines, partners, travel agencies, and service providers. Transactions such as ticket sales, ancillary services, and commissions are recorded in real time.
Aviation software integrated with blockchain reduces payment disputes, speeds up settlements, and improves financial accuracy across complex airline ecosystems.
10] Loyalty Programs and Customer Rewards Management
Blockchain enables secure, interoperable loyalty programs across airlines and partners. Reward points can be tracked, redeemed, and transferred transparently without duplication or fraud.
Aviation software using blockchain simplifies loyalty management, enhances customer trust, and allows seamless integration with hotels, car rentals, and other travel services.
Blockchain is one of the aviation technology trends that should be followed effectively.
Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain in the Aviation Industry
If you want to lead the aviation industry, you need to evaluate the competitors and their strategy to utilize blockchain technology. This will help you learn how blockchain is helpful in the aviation sector and how you can explore this technology to your advantage.
Let’s learn more about the real-world cases in this section.
Case Study 1: Airbus
Airbus uses blockchain to secure aircraft data sharing between airlines, OEMs, and maintenance providers.
Through initiatives like FlightChain, blockchain ensures data ownership, prevents tampering, and enables trusted collaboration across the aviation ecosystem without central control.
Case Study 2: SITA
SITA applies blockchain to passenger identity management and baggage tracking.
Blockchain in aviation enables verified data exchange between airlines, airports, and border agencies, reducing identity fraud, enhancing border clearance, and facilitating seamless passenger journeys.
Case Study 3: Honeywell Aerospace
Honeywell uses blockchain in aviation to authenticate aircraft parts and track component lifecycle data.
Each part’s origin, certification, and maintenance history is stored immutably, helping airlines prevent counterfeit components and meet strict safety regulations.
Case Study 4: Lufthansa Industry Solutions
Lufthansa Industry Solutions implements blockchain in MRO documentation systems. Hence, one of the roles of blockchain in aviation software is providing safety in MRO documentation.
Maintenance logs, inspection reports, and compliance records are stored on blockchain to ensure audit readiness and eliminate discrepancies during regulatory inspections.
Case Study 5: IBM
IBM provides blockchain platforms used by aviation companies for supply chain transparency and maintenance record integrity.
Blockchain ensures all stakeholders have access to a single, trusted version of operational data across parts manufacturing and servicing.
Case Study 6: GE Aviation
GE Aviation explores blockchain for secure sharing of aircraft health and engine performance data.
Blockchain in the aviation industry enables trusted data exchange between airlines, lessors, and service teams while protecting sensitive operational information.
Case Study 7: SAP
SAP integrates blockchain into aviation ERP systems for parts traceability, contract automation, and supplier coordination.
Aviation businesses use blockchain-enabled workflows to reduce reconciliation delays and improve transparency across vendors.
Case Study 8: Winding Tree
Winding Tree applies blockchain to airline distribution and ticketing systems. Blockchain in aviation software, as in Winding Tree, helps to enhance the user experience.
It removes intermediaries, allowing airlines to control inventory, pricing, and settlements directly, while reducing distribution costs.
How can Aviation Companies Start Implementing Blockchain?
When you begin with the aviation software features, blockchain cannot be ignored. You can start by identifying high-impact use cases, defining business and compliance requirements, selecting the right blockchain architecture, and then scaling the blockchain software.
Let’s evaluate the complete steps to start implementing blockchain in aviation software in this section.
Step 1: Identify High-Impact Use Cases
Start by pinpointing operational pain points where blockchain adds real value, such as MRO records, parts traceability, identity verification, or financial settlements.
Prioritize use cases with high data sensitivity or multiple stakeholders. Clear use case selection prevents overengineering and keeps adoption focused.
Step 2: Define Business and Compliance Requirements
Aviation operates under strict regulatory frameworks. Clearly define data privacy, security, audit, and compliance needs before selecting any blockchain model.
Align blockchain goals with aviation authorities and internal governance to avoid rework later.
Step 3: Choose the Right Blockchain Architecture
Decide between public, private, or consortium blockchain based on data access and trust levels.
Most aviation use cases benefit from permissioned blockchains that control participant access. Architecture choices directly impact scalability, performance, and integration complexity.
Step 4: Integrate Blockchain with Existing Aviation Software
Blockchain should complement, not replace, current aviation systems. Integrate it with MRO platforms, ERP systems, booking engines, and identity management software.
Smooth integration ensures continuity while adding transparency and security.
Step 5: Start with a Pilot or Proof of Concept
Begin with a controlled pilot project involving limited stakeholders and data sets. This helps validate technical feasibility, performance, and regulatory alignment.
A successful proof of concept builds confidence before scaling blockchain across operations.
Step 6: Focus on Security, Governance, and Data Ownership
Define who can access, update, and validate data on the blockchain network. Implement strong identity controls, encryption, and governance policies.
Clear ownership models protect sensitive aviation data and maintain trust among participants.
Step 7: Scale Gradually and Train Teams
Once validated, expand blockchain use across departments or partners. Train technical teams and operational staff to manage blockchain workflows effectively.
Gradual scaling reduces risk and ensures long-term adoption success.
Challenges for Adopting Blockchain in Aviation Software
The challenges for adopting blockchain in aviation software include regulatory and compliance uncertainty, scalability and performance limitations, data privacy and access control challenges.
Let’s learn all the challenges of adopting blockchain in aviation software, below.
► Integration with Legacy Aviation Systems
Most aviation software runs on legacy systems built over decades. Integrating blockchain with existing MRO, ERP, booking, and air traffic systems is technically complex.
Poor integration can disrupt operations, increase costs, and slow adoption across stakeholders.
► Regulatory and Compliance Uncertainty
Aviation is heavily regulated, and blockchain adoption often outpaces clear regulatory guidance. Data ownership, cross-border data sharing, and audit standards vary by region.
This uncertainty makes airlines and airports cautious about large-scale blockchain deployments.
► Scalability and Performance Limitations
Aviation systems process massive volumes of real-time data. Blockchain networks may struggle with transaction speed, latency, and throughput at scale.
Without careful architecture planning, performance bottlenecks can impact mission-critical aviation software workflows.
► High Implementation and Operational Costs
Blockchain adoption involves infrastructure setup, skilled talent, security controls, and ongoing maintenance.
These costs can be high, especially for enterprise-grade aviation software. Budget constraints often slow adoption despite long-term efficiency gains.
► Data Privacy and Access Control Challenges
Aviation data includes sensitive passenger, operational, and security information. Ensuring privacy while maintaining blockchain transparency is complex.
Poor access control design can lead to compliance risks or unintended data exposure.
► Industry-Wide Collaboration and Adoption Barriers
Blockchain delivers maximum value when multiple stakeholders participate. Airlines, airports, regulators, and suppliers must agree on shared standards.
Achieving industry-wide collaboration is difficult and often slows network adoption.
Looking to Build Secure, Blockchain-Driven Aviation Systems with JPLoft?
Aviation systems demand secure data, regulatory compliance, and seamless coordination across multiple stakeholders. Blockchain enables trusted data sharing, tamper-proof records, and automated workflows that strengthen aviation software reliability and transparency.
JPLoft helps aviation businesses turn these advantages into real, scalable solutions. As an experienced aviation software development company, JPLoft builds secure, blockchain-driven aviation systems designed for compliance, performance, and long-term growth. From MRO platforms to supply chain tracking and smart contracts, the focus remains on stability, scalability, and future readiness.
JPLoft works as a long-term technology partner for aviation organizations looking to modernize complex systems with confidence. The team combines deep technical expertise with a clear understanding of aviation operations to deliver solutions that integrate smoothly with existing infrastructure.
The company brings a consultative, engineering-led approach to aviation software development, helping organizations move from legacy systems to modern digital platforms with minimal risk. The team emphasizes clear architecture, secure data handling, and regulatory alignment from day one.
Conclusion
Blockchain is steadily reshaping how the aviation industry manages data, trust, and collaboration. From aircraft maintenance and supply chain traceability to passenger identity, compliance, and revenue settlement, blockchain introduces transparency, security, and automation across aviation software systems.
As adoption grows, airlines and aviation stakeholders who plan early gain stronger control over data integrity, operational efficiency, and regulatory readiness. While challenges around integration, scalability, and compliance remain, a structured implementation approach helps reduce risk.
For aviation businesses aiming to build future-ready systems, blockchain is no longer experimental. It is becoming a strategic foundation for secure, scalable, and resilient aviation technology ecosystems.
FAQs
Blockchain enables secure data sharing, immutable records, and automated workflows across aviation operations, including maintenance, supply chain, identity, compliance, and settlements.
It helps multiple stakeholders collaborate without relying on a single central authority.
Blockchain ensures accurate, tamper-proof maintenance and parts records, reducing counterfeit components and data manipulation.
Aircraft maintenance, MRO, supply chain management, passenger identity, regulatory audits, loyalty programs, and financial settlements benefit the most.
These areas involve high data sensitivity and multi-party coordination.
Yes, blockchain can integrate with existing aviation systems using APIs and middleware without replacing core platforms.
This allows airlines and airports to adopt blockchain gradually with minimal disruption.
Key challenges include legacy system integration, regulatory uncertainty, scalability limits, high implementation costs, data privacy concerns, and collaboration barriers.
Addressing these early is critical for successful long-term adoption.
They should begin with high-impact use cases, define compliance needs, choose permissioned architectures, and run pilot projects. Gradual scaling with proper governance and team training ensures sustainable implementation.










Share this blog